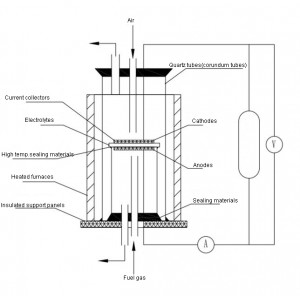
Solid Oxide Fuel Cell Evaluation System
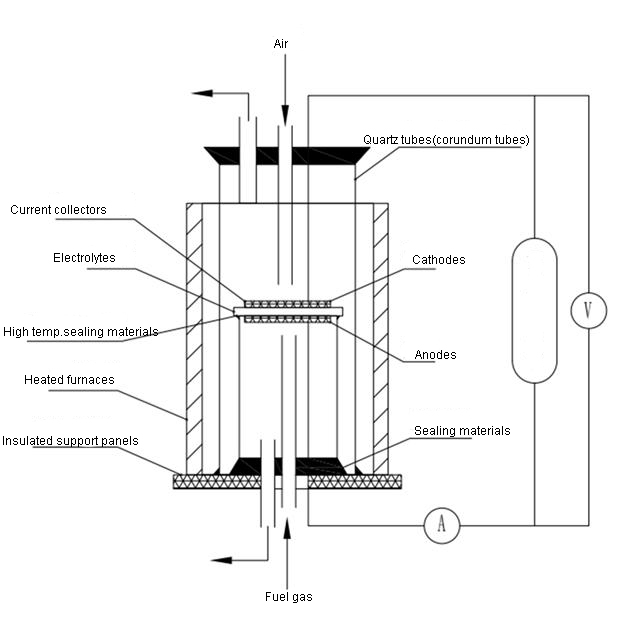
Solid oxide fuel cell (SOFC), the electrolyte used in SOFC is a solid non-porous metal oxide, usually yttrium trioxide-stabilised zirconium dioxide (Y2O3-stabilised-ZrO2, YSZ), and the oxygen ions within the electrolyte at an operating temperature of 650~1000°C have a high conductivity. The material used for the anode is nickel-zirconia cermet (Ni-YSZ) and the cathode is strontium-doped lanthanum manganate (Sr-doped-LaMnO3, LSM).
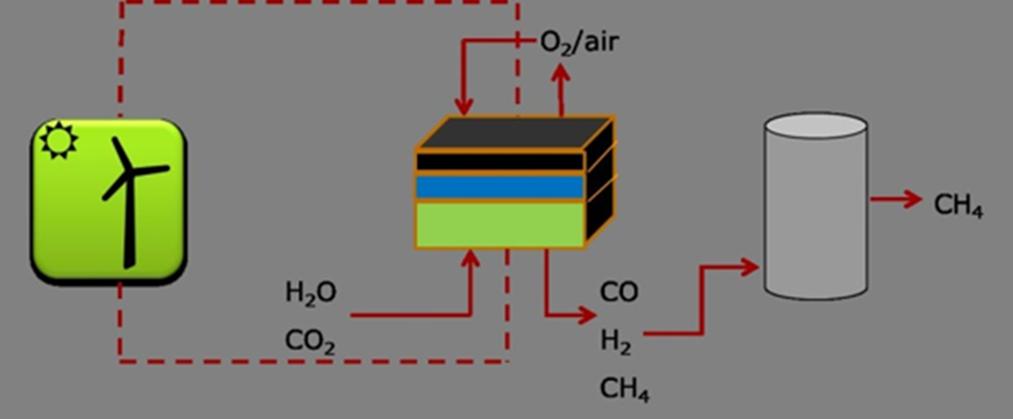
Advantageous features of SOFC: because of the all-solid structure of the battery, it avoids the problems of corrosion and electrolyte leakage caused by the use of liquid electrolyte; it does not use platinum and other precious metals as catalysts and greatly reduces the cost of the battery; the high-quality waste heat of SOFC can be used for cogeneration, thus improving the utilization rate of the waste heat, and the total power generation efficiency of up to 80% or more; the fuel has a wide range of applications, and, from the principle of solid oxide ionic conductor is the most ideal. Wide range of fuel application, in principle, solid oxide ionic conductor is the most ideal electrolyte material for transferring oxygen, so SOFC is suitable for almost all combustible fuels, not only gas, carbon monoxide, methane and other fuels, but also natural gas, coal gas and other hydrocarbons can be used directly as fuel.
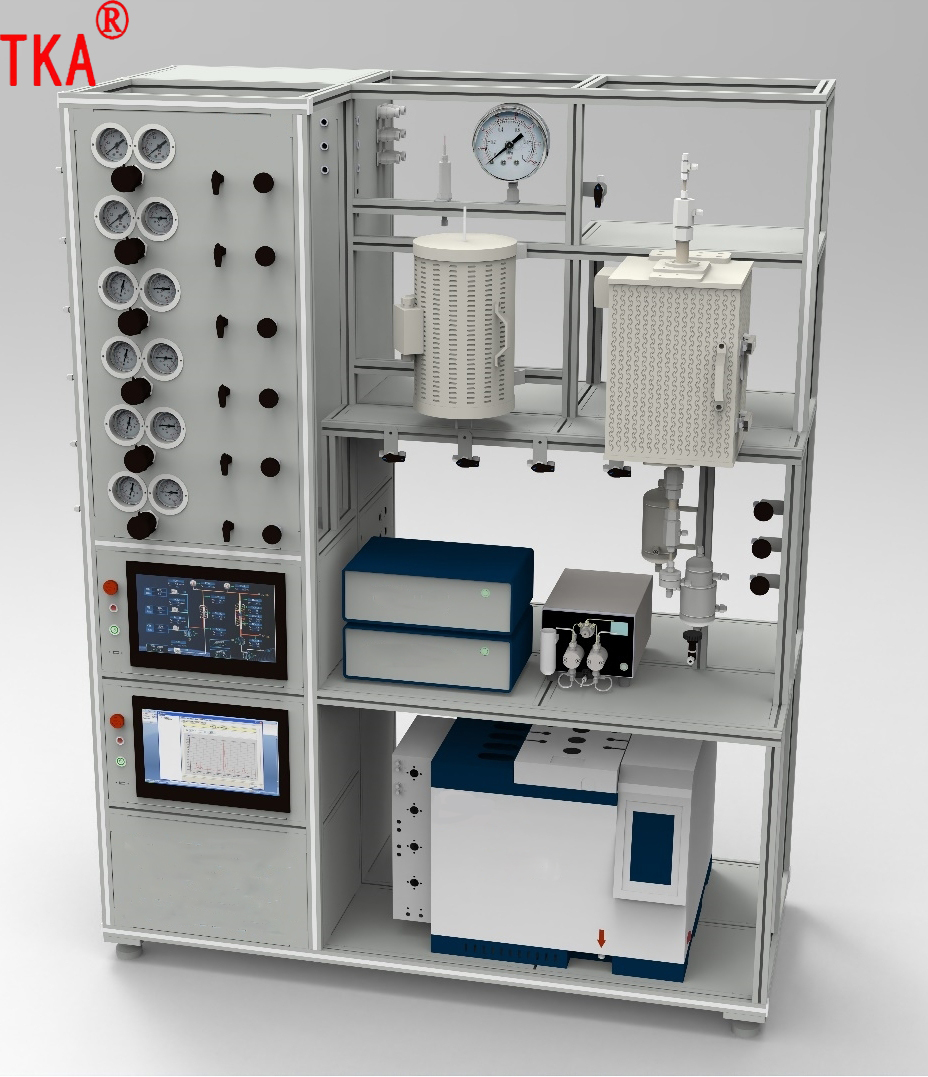
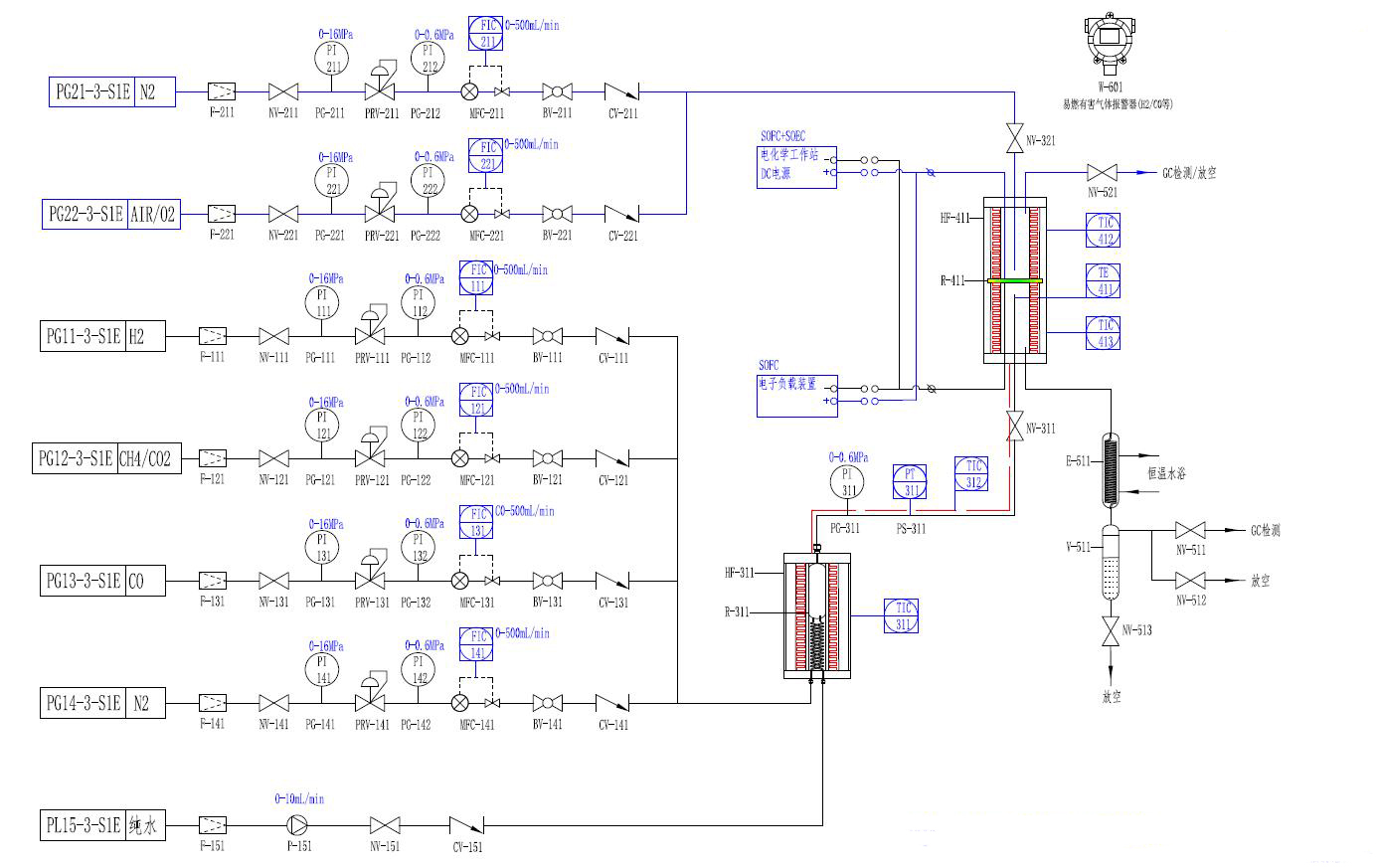
The TKSC-SOFC80 Solid Oxide Fuel Cell Evaluation System is used to evaluate the electrochemical performance, stability and efficiency of SOFC single cells or stacks, and to clarify the key influencing factors (materials, temperature, fuel composition, etc.). The system is capable of precisely controlling the operating conditions (temperature, gas composition, flow rate, etc.), monitoring the electrochemical performance (voltage, current, impedance, etc.) in real time, and analysing the reaction products (H2O, CO2, O2, etc.). This SOFC evaluation system is scientifically designed and comprehensively functional, capable of meeting a wide range of testing needs from material research to system integration. With high-precision control and multi-functional test modules, it can provide reliable data support for SOFC performance optimisation and commercial application.
1) Measure polarisation curves (I-V-P curves) and power density at different temperatures (600-900°C).
2. Analyse the effect of fuel utilisation (H2/CH4) on battery efficiency and output performance.
3. resolve ohmic impedance, activation polarisation and concentration polarisation contributions by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS).
4. assess decay mechanisms (e.g. anode carbon build-up, electrolyte aging) in long-term operation (>100 h).
5. Common fuel gases: H2, CH4, syngas (H2/CO), air (oxidiser).
6) Electrochemical workstations, electronic loads (for I-V, EIS testing).
7) Gas Chromatograph (GC) or Mass Spectrometer (for fuel utilisation analysis).
8.Data acquisition system (real-time recording of temperature, voltage and current).
9. It can comprehensively evaluate the electrochemical performance and reliability of SOFC and provide experimental basis for material optimisation and system integration.